A recent update from the Ministry of Health has confirmed 38 cases of Mpox across 12 counties since the outbreak was declared on July 31, 2024, with one fatality reported.
Half of the cases involve individuals with a travel history to Mpox-affected nations, including Uganda and Rwanda.
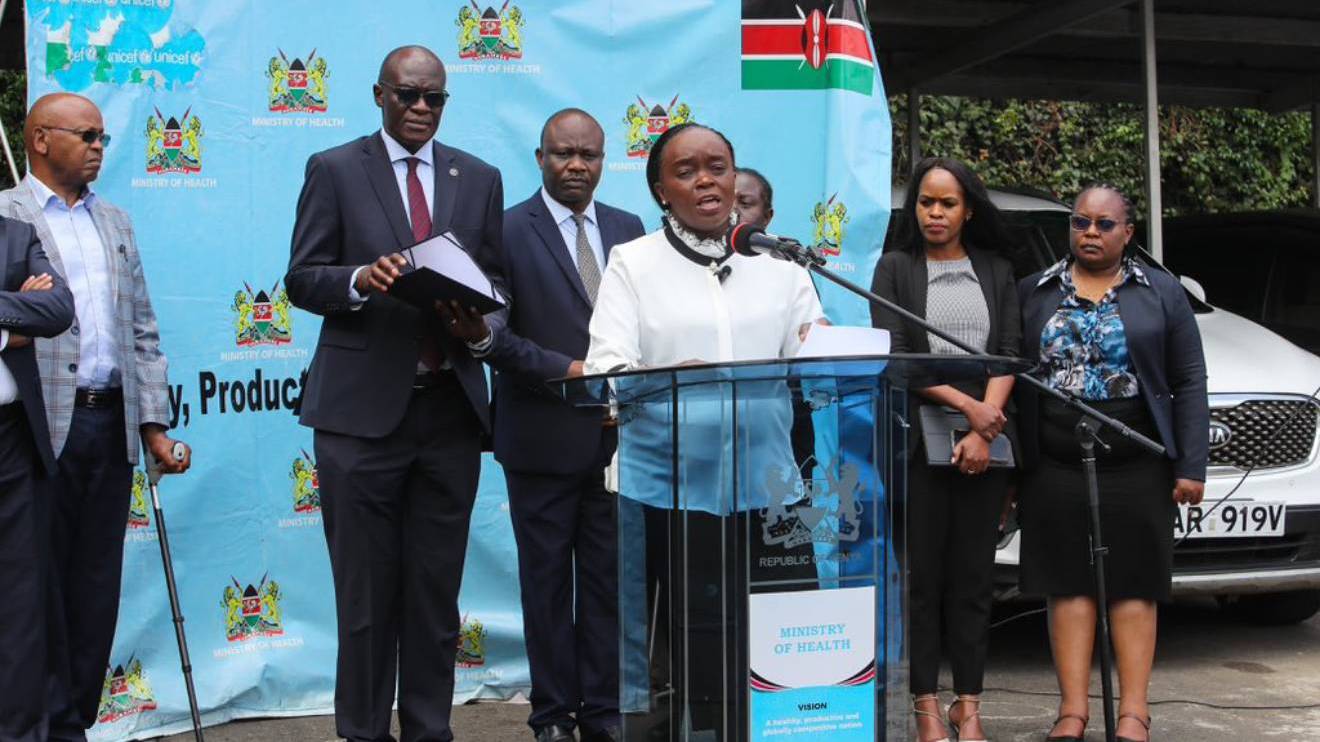
Dr. Patrick Amoth, Director General for Health, outlined the government’s response efforts, including the activation of the Public Health Emergency Operations Centre (PHEOC) and County Emergency Operations Centres (EOCs).
“To ensure a coordinated approach, we have activated the Public Health Emergency Operations Centre (PHEOC) and repurposed the Mpox task force to oversee the Ebola response,” Amoth said.
The ministry has also developed case management and infection prevention guidelines, rolled out mental health support services, and intensified risk communication campaigns.
Read More
Screening at points of entry has been a key focus, with over 3.2 million travellers screened. However, response efforts have been hampered by low public risk perception and inadequate isolation facilities.
To address these challenges, the Ministry of Health plans to enhance public awareness, strengthen county isolation facilities, and expand community engagement.
Discussions with the World Health Organization (WHO) and Africa CDC are ongoing to facilitate access to Mpox vaccines.
Meanwhile, Kenya remains on high alert for a possible Marburg Virus Disease (MVD) outbreak following cases in Tanzania’s Kagera region.
Given the frequent cross-border movement, the Ministry of Health has reinforced preparedness measures to prevent an outbreak within Kenya.
During a weekly media briefing, Cabinet Secretary for Health Dr. Deborah Barasa outlined the government’s contingency plan, which includes heightened surveillance, enhanced screening at border points, activation of laboratory networks, and the development of case management protocols.
Infection prevention and control training for healthcare workers has also been prioritised, alongside the distribution of protective gear.
Kenya is collaborating with Tanzanian health authorities, WHO, and Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) to strengthen disease surveillance and technical support.
Dr. Amoth urged all counties and health facilities to remain vigilant, strictly adhere to infection prevention protocols, and ensure continuous readiness to manage potential MVD cases.
With these measures in place, Kenya aims to curb the spread of Mpox while proactively safeguarding the country against a possible Marburg virus outbreak.


 (1)-1727972556.jpg)





-1715610534.jpeg)
